How to setup environment variables in oracle to successfully
connect to a particular database/instance
Oracle environment variable is set so that your operating system
(OS) can know the Oracle software installation directory and which oracle
software/binaries should interact with which database/instance.
The most important environment variable are listed below
ORACLE_HOME : setting oracle home means which oracle product/software or
installation you will be using to associate with your databasehaving oracle
home environment variable makes easier for maintenance and management of oracle
software.As per Oracle optimal flexible architecture (OFA)
/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/dbhome_1
ORACLE_SID : The oracle system identifier is a unique identifier
which is set to interact with a particular instance. You may have multiple
oracle database on a single machine by setting this variable we are information
oracle software to connect to that particular instance.
we will learn various way to set this variable
firstly we will check oracle home and how many databases are
installed on the machine
[oracle@db10g /]$ cat /etc/oratab
#
# This file is used by ORACLE utilities. It is created by root.sh
# and updated by the Database Configuration Assistant when creating
# a database.
# A colon, ‘:’, is used as the field terminator. A new
line terminates
# the entry. Lines beginning with a pound sign, ‘#’, are comments.
#
# Entries are of the form:
# $ORACLE_SID:$ORACLE_HOME:<N|Y>:
#
# The first and second fields are the system identifier and home
# directory of the database respectively. The third filed indicates
# to the dbstart utility that the database should , “Y”, or should not,
# “N”, be brought up at system boot time.
#
# Multiple entries with the same $ORACLE_SID are not allowed.
#
#
ora10gdb01:/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01:N
10gdb02:/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01:N
In the above out put we can see we have two databases ora10gdb01
& 10gdb02
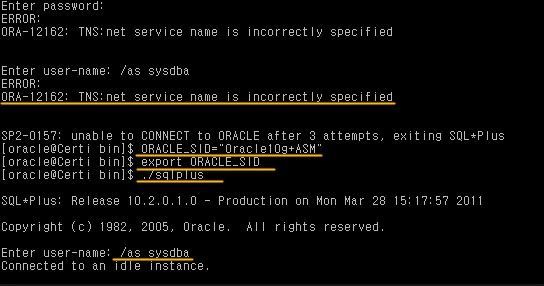
now let see if our environment variable is not set correctly
what will happen
Login: oracle
Last login: Sat May 31 18:12:45 2014 from 192.168.1.1
[oracle@db10g ~]$ sqlplus
-bash: sqlplus: command not found
[oracle@db10g ~]$
the operating system doesn’t know what is sqlplus command
setting oracle home and sid for ora10gdb01 manually
set oracle_sid by giving below command
[oracle@db10g /]$ export ORACLE_SID=ora10gdb01
check if the environment variable is set correctly
[oracle@db10g /]$ echo $ORACLE_SID
set oracle_home by giving below command
[oracle@db10g /]$ export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01
check if the environment variable is set correctly
[oracle@db10g /]$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01
now you can connect to the database issuing below
[oracle@db10g /]$ sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 – Production on Sat May 31 20:07:18
2014
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to an idle instance.
SQL>
using .oraenv script provided by oracle, installed during
software installation
[oracle@db10g ~]$ . oraenv
ORACLE_SID = [ora10gdb01] ? ora10gdb01
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_SID
ora10gdb01
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01
let us again login as oracle user and check the environment
variables
Login: oracle
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_SID
[oracle@db10g ~]$
as you can see, there is
no output that means that our environment variables are not set
now we will again use .oraenv to set environment variable for
our second database
[oracle@db10g ~]$ . oraenv
ORACLE_SID = [oracle] ? 10gdb02
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0.1/db01
[oracle@db10g ~]$ echo $ORACLE_SID
10gdb02
[oracle@db10g ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 – Production on Sat May 31 20:27:10
2014
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to an idle instance.
SQL> startup